安全蛋白質在特殊教槽料的使用
1. 最新小豬飼養管理的趨勢
※早期離乳分開飼養(Segredated Early Weaning, S.E.W.)
※S.E.W.必需靠整個小豬的營養、疾病及免疫和畜舍環境的配合。
※其操作過程如下:
(1)小豬10~12天早期離乳。
(2)然後移到統進統出消毒過的離乳豬舍,其豬舍必需離開其分娩豬舍3公里以上,然後再養到25~30公斤。
(3)最後再移到肉豬舍,直到上市。
※S.E.W.飼養體系主要與現今小豬飼養體系的不同考慮點:
(1)極早期離乳,其考慮因素為小豬的被動免疫與自身主動免疫消長情況,如圖1可明顯看出10~12天離乳,可降低母豬對小豬的垂直感染,16日齡的小豬因被動免疫與主動免疫都低,非常容易被母豬感染,而爆發疾病。

(2)離乳小豬舍與母豬分娩舍的最少距離,視主要疾病而有不同,如下表所示:
| Multi-Site Production-Farm Locations. The estimated distances for several diseases as advised by American Veterinarians. |
|
| Disease | Km |
| Mycoplasmal pneumonias | 3.5 |
| P.R.R.S. | 3.5 |
| Strepsuis(via flies) | 2.0 |
| Swine Influenza | 5.0~7.0 |
| Aujeszky's Disease | 42.0 |
| Foot and Mouth | 42.0 |
| T.G.E. (via birds) | 70.0?? |
| Source:Carlson(1994). | |
(3)所以,按不同疾病的最佳離乳天數如下:
| Maximum Weaning Age To Eliminate Organism | |
| Organism | Weaning Age(days) |
| Aujeszky's Disease | 21 |
| Actinobacillus pleuropneumonia(APP) | 21 |
| Mycoplasma pneumonia | 10 |
| Pasteurella multocida | 10 |
| Haemophilus parasuis(HPS) | 14 |
| P.R.R.S. | 10 |
| Salmonella choleraesuis | 12 |
| T.G.E. | 21 |
| A.R. | 14 |
| Source:Yeske(1994). | |
※S.E.W.與現今小豬飼養體系的比較:
(1)飼養效果:
| Performance of S.E.W. Pigs Versus
Conventionally Reared Controls. (2)Very Good Performance-Controls. |
|||||
| CONTROLS | S.E.W. | % Improvement |
|||
| Day | Kg | A.D.G., g | Kg | A.D.G., g | |
| 7 | 2.38 | 161 | 2.60 | 173 | 9 |
| 21 | 5.24 | 190 | 5.89 | 215 | 12 |
| 35 | 8.95 | 220 | 11.14 | 279 | 25 |
| 49 | 14.06 | 261 | 18.81 | 356 | 34 |
Source:Gadd(1994)Client's Records(U.S.A.) |
|||||
| Performance S.E.W. Pigs Versus Conventionally
Reared Controls. (1)Modest Performance-Controls. |
|||||
| CONTROLS | S.E.W. | % Improvement |
|||
| Day | Kg | A.D.G., g | Kg | A.D.G., g | |
| 7 | 2.27 | 146 | 3.63 | 340 | 93 |
| 21 | 4.54 | 157 | 5.50 | 262 | 21 |
| 35 | 8.17 | 198 | 14.10 | 367 | 73 |
| 48 | 12.16 | 229 | 21.80 | 428 | 78 |
| 63 | 22.25 | 333 | 35.87 | 550 | 61 |
| 77 | 29.26 | 373 | 49.49 | 626 | 69 |
Source:After Dritz(1994). |
|||||
(2)屠體瘦肉的經濟效果:
| Where cost per tonne is related to extra meat sold per tonne of feed at slaughter. The high cost of pre-starters falls into perspective. | |||
| Correct early weaned pre-starters per tonne. | Amount eaten per piglet (kg) |
Extra cost per piglet | |
| Stage 1 | 120 p/kg | 2.27 | |
| Stage 2 | 85 p/kg | 2.75 | |
| Stage 3 | 75 p/kg | 2.70 | US$1.87 |
| Assuming 3.25 pigs per tonne of feed at
slaughter: Extra Investment per 3.25 piglets=US$1.87×3.25=US$6.08 Extra Yield of Meat per tonne at slaughter=20kg Value =$19 |
|||
| Source:Clients records(U.S.A.) | |||
※S.E.W.飼養方法及其產品營養濃度如下:
| Proposed S.E.W. Feeding Regime For U.S. Conditions(1995) | ||||
| Pig weight, kg | DE(MJ) | Lysine, (Total) | Lys.:DE | Typical FCR |
| 2.50~5.00 | 17.5 | 1.75 | 1:1 | 1:1.10 |
| 5.00~7.25 | 16.5 | 1.70 | 1.02:1 | 1:1.16 |
| 7.25~9.60 | 15.7 | 1.50 | 1:1 | 1:1.22 |
| 9.60~19.6 | 15.0 | 1.45 | 0.98:1 | 1:1.30 |
| Pig weight, kg | Feed Intake, g | DE Intake, MJ | Lys.Intake, g | |
| 2.50~5.00 | 172 | 3.0 | 3.0 | |
| 5.00~7.25 | 290 | 4.8 | 4.9 | |
| 7.25~9.60 | 440 | 7.0 | 7.0 | |
| 9.60~19.6 | 700 | 10.7 | 10.5 | |
Source:Toplis(1995), personal communication. |
||||
| Recommended Feeding Programme for S.E.W. in The U.K. | ||
| Recommended | Optional | |
| Birth | All piglets dosed with a colostrum substitute soon after birth. |
|
| Day 2-6 | Offer small quantities of pasteurised piglet conditioner(PPC)- |
Offer sow milk equivalent at 76g/litre. |
| Day 7-Weaning | Offer 50:50 PPC and "pre" pre-starter meal. | |
| Weaning-W+3days | "Pre" pre-starter pellets or meal+porridge(twice daily) |
|
| Day W+4-W-7 days | "Pre" pre-starter pellets or meal. |
Piglet porridge as necessary. |
| Day W+8-Day 21(age) | "Pre" pre-starter pellets or meal. |
|
| Day 21 (age) | Normal feeding regime. | |
2. 特殊早期教槽料的考慮因素:
※高品質原料的選擇如下:
| Some examples of ingredients used in piglet diets. | |
| Protein sources for piglet diets | Energy sources for piglet diets |
Milk Proteins Casein Skim 2A (grassmeal 8%) Skim 2B(fish 10%,grass 4%) Whey products Animal proteins Herring meal LT fish meal Egg protein Spray dried orcine plasma Blood meal Vegetable proteins Potato protein Hipro soy ext Full-fat soy Soy protein concentrate Processed soy (i.e. soy flour, soy isolate) Synthetic amino acids Lysine Methionine Threonine Tryptophan |
Cereals Cooked maize Cooked wheat Cooked barley Porridge oats Carbohrdrates Sucrose Glucose Lactose Oils Coconut oil Soybeal oil Fat-filled milk product Byproducts Oat byproduct Sweet biscuit meal Maize byproduct'
|
※原料的消化率與攝食量的關係:
| Diet digestibility | Voluntary food intake kg per day |
| 0.85 | 0.87 |
| 0.80 | 0.65 |
| 0.75 | 0.52 |
※不同蛋白質原料消化率與氮在糞便中及迴腸中的消化率和其內源性氮的流失關係:
| Nitroge digestibility and endogenous N losses of young piglets fed diets based on four different protein sources. | ||||
| N digestibility, % | SMP | SBM | SI | FM |
| Apparent fecal | 94.0 | 84.0 | 90.7 | 89.1 |
| Apparent ileal | 84.4 | 76.5 | 78.4 | 73.0 |
| True fecal | 97.3 | 93.5 | 98.1 | 96.4 |
| True ileal | 92.7 | 90.6 | 98.4 | 89.3 |
| Endogenoug fecal N losses(mg per day) | 315 | 963 | 715 | 697 |
| Endogenoug ileal N losses(mg per day) | 786 | 1,422 | 1,970 | 1,558 |
SMP=Skimmed milk powder, SBM=Soybean isloate, SI=Soy isolate, FM=Fish meal Source:Extrapolated from Makkink 1993d. |
||||
| Approximate relative activities of the major digestive enzymes in sucked piglets at birth and at the time of peak lactation in the sow. | ||
| Enzyme | Activity, % of value at digestive maturity | |
| Birth | 3 weeks | |
| Trypsin | 10 | 10 |
| Chymotrypsin | 60 | 100 |
| Pancreatic lipase | 8 | 48 |
| Pancreatic amylase | 0 | 3-30 |
| Lactase | 300-600 | 100 |
| Cucrase | 0 | 25 |
| Maltase | 0-5 | 20 |
| Small-intestinal dipeptidases | 200 | 100 |
3. 高品質教槽料對離乳小豬和肉豬上市天數的影響
| 離乳重量影響性能 | ||
| 離乳重量,磅
|
重量(磅) 28 |
離乳後天數 56 |
| 10~11 12~13 14~15 16~17 18~20 |
27.1 30.6 33.3 35.7 37.9 |
60.8 66.5 70.0 74.6 77.8 |
Kansas State University, 1992. |
||
| 離乳後第一週性能影響往後之性能 | ||||
| 每一週每日增重,磅 | 重量(磅),天數 | 上市a | ||
| 28 | 58 | 156 | 日齡 | |
| ≦0 0~0.33 0.33~0.50 >0.50 |
32.4 35.3 37.3 40.1 |
66.3 70.2 71.6 76.6 |
232.2 238.4 245.1 249.8 |
183.3 179.2 175.2 173.0 |
a. 達240磅日齡(Kansas State University, 1992.) |
||||
4. 小豬出生死亡與出生體重和離乳前死亡率的分析
| Mean birth weights for surviving piglets, stillborn piglets and those dying after birth. | |||
| Group | No. of piglets | Birth weight, kg | s.d. |
| Stillborn | 691 | 1.17 | 0.40 |
| Died 0-3 weeks | 1123 | 1.19 | 0.40 |
| Died 3-6 weeks | 178 | 1.39 | 0.36 |
| Died 6-9 weeks | 94 | 1.40 | 0.34 |
| Surviving at 9 weeks | 6048 | 1.46 | 0.32 |
| Neonatal mortality for different species | |
| Species | Neonatal moratality, % |
| Pig | 13(5~20) |
| Human | 2(1.5~7) |
| Cattle | 4(0~10) |
| Sheep | 5(3~8) |
5. 早期離乳教槽料蛋白質原料的比較優缺點:
| 乳製品 | 44%黃豆粉 | 脫殼黃豆粉soy flour | 高蛋白黃豆粉soya protein concentrate | 一般 紅或白魚粉 |
L/T魚粉 | 魚溶粉 fish protein concentrate |
|
| 1. 消化率 | ++++ | + | ++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | +++ |
| 2. 適口性 | ++++ | ± | + | ++ | ++ | +++ | +++ |
| 3. 價格 | --- | +++ | + | - | ++ | + | -- |
| 4. 毒性 | +++ | -- | - | ++ | ± | + | + |
| 5. 病原菌的污染性 | ± | - | + | ++ | -- | ± | ± |
| 6. 氨基酸組合 | +++ | ± | + | + | + | + | ++ |
| 7. 來源穩定性 | -- | +++ | ++ | ++ | -- | -- | -- |
在此特別介紹高蛋白黃豆粉(soya protem concentrate, S.P.C.), 此原料的製造流程及其營養
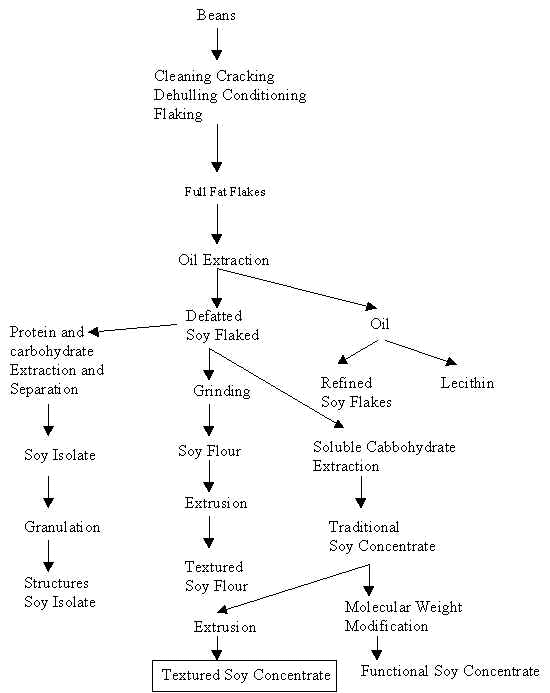
PROFINE Ⅱ
| Physical Properties Apperance and color Size of particles Wettability and stability in aqueous phase Standard Analysis in g /100g product Protein (dry matter ; Nx 6.25) Protein (as is basis) Moisture Fat Ash Crude Fiber Minerals, % Calcium Total phosphorus Sodium Potassium Magnesium Minerals parts per million Iron Copper Zinc Amino Acid Content( g / 100g product) Lysine Methonine Cystine Threonine Leucine Isoleucine Phenylalanine Tyrosine Tryptophan Histidine Valine Biological Analysis Microbial Count : (per g) Total Count E. coli(per g) Salmonella(per 200g) Trysin Inhibitor activity Urease Antigens Packaging |
Fine granules, cream color Smaller than 250 microns:less than 8% Not applicable. This product intended for inclusion in feed to be fed dry.
70 min 64 in 10 max 0.3 min 7 4.5
0.35 0.81 0.05 2.20 0.32
100-120 13 30
4.2 0.9 1.0 2.8 5.2 3.2 3.3 2.5 0.9 1.7 3.4
less than 10,000 Negative None detected Less than 3 mg trypsin inhibited per g of product Less than 0.1 mg. Nitrogen per g of product per min. at 3℃ None detected 50 lbs. |
【一般黃豆粉(44%)主要抗營養成份】
※glycinin
※β-glycinin
※urease尿素酵素
※Trypsin Inhibitor抗胰蛋白分解酵素
※Lecitin血球凝集物
以上抗營養成份,主要作用於幼小動物的胰蛋白質分解酵素的分泌,抑制蛋白質的消化,破壞小腸乳糜管,而增加消化道內源性氮排出。
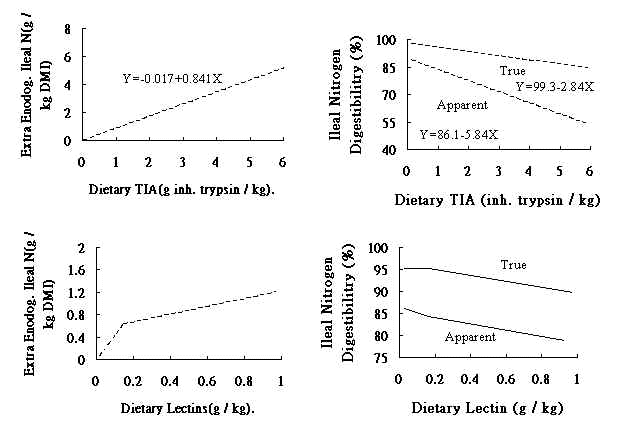
以上就是為什麼44%黃豆粉添加於小豬教槽料中,容易造成下痢、適口性不佳、營養吸收不良,甚至造成二次病原菌的感染。另外,44%黃豆粉含有黃豆殼(內含有中性纖維素N.D.F.),造成長幼小動物的蛋白質維持量增加,如此剩下的蛋白質對生長及造肉相對減少,對現今精肉型的豬生長發育影響很大,如下表:
| The effect of dietary factors on extra nitrogen requirements for maintenance | ||||
| Nitrogen requirement for | ||||
| Maintenance | Dietary NDF | Dietary TA | Dietary Lectins | |
| Gram day | 2.04 | 0.58 | 0.40 | 0.35 |
| Relative to maintenance, % | 100 | 28.4 | 19.6 | 17.2 |
以上種種44%黃豆粉配方,所造成內源性氮的排出及蛋白質維持量增加,都會造成羥丁胺酸與離胺酸比值提高。
高蛋白黃豆粉(S.P.C.)的使用及其效果,因為早期離乳教槽料,除了要考慮原料品質外,一定要注意儘量減少抗營養成份的含量。所以,高品質教槽料不能使用44%黃豆粉,應改用高蛋白黃豆粉(S.P.C.)來配合其他乳製品,以減低原料抗營養成份的影響。
| Diet Composition and Calculated Analyses | ||||
| Skim milk | Soybean meal | SPC 1 | SPC2 | |
Ingredient, % Dried skim milk Dehulles soybean meal Soy protein concentrate Corn Rolled oat groats Dried Whey Lactose Fat blend Other ingredients Calculated Analyses, % Protein Lysine Fat Fiber |
35.0 -- -- 10.0 29.1 20.0 -- 4.8 1.1
19.4 1.35 7.0 1.0 |
-- 38.1 -- 7.5 11.7 -- 31.5 7.7 3.5
20.8 1.35 8.9 1.8 |
-- -- 24.1 7.5 27.1 -- 31.5 6.4 3.4
20.5 1.35 8.2 1.7 |
-- -- 24.1 7.5 27.1 -- 31.5 6.4 3.4
20.5 1.35 8.2 1.7 |
| Camparsion of Soy Protein Concentrates to Skim Milk and Soybean meal on Performance | ||||
| Item | Skim milk | Soybean meal | SPC 1 | SPC 2 |
| Avg daily gain, g Week 1 Week 2 Weeks 1and 2 |
173 245 209 |
127 204 166 |
150 200 175 |
160 250 205 |
| Avg daily feed intake Week 1 Week 2 Weeks 1and 2 |
213 248 231 |
204 267 236 |
232 266 249 |
218 285 252 |
| Feed/gain Week 1 Week 2 Weeks 1and 2 |
1.46 1.05 1.11 |
1.96 1.44 1.42 |
1.64 1.35 1.42 |
1.67 1.18 1.22 |
| Camparsion of Soy Protein Concentrates to Skim Milk and Soybean meal on Digestibility and gut Morphology | ||||
| Item | Skim milk | Soybean meal | SPC 1 | SPC 2 |
Digestibility Dry Matter, % Nitrogen, % |
88.5 83.0b |
87.3 79.7c |
88.6 81.4bc |
89.8 85.7b |
Morphology/Antibody Titer Villus height, um Crypt Depth, um Villus area, um2 Anti-soy antibody, log2 |
266b 198c 26915b 3.86 |
175d 222b 16945c 6.67c |
207c 214c 22191b 6.67b |
230c 196c 21563b 4.25b |
| Camparsion of Central Soy Specially-Processed Soy Protein Concentrate to Soybean Meal | ||
| Soy Concentrate | Soy meal | |
| Daily gain, 0-14 days | 0.46 | 0.36 |
| Daily intake, 0-14 days | 0.56 | 0.52 |
| Feed/gain, 0-14 days | 1.42 | 1.70 |
| Antigen titer in gut contents | 0.0 | 1.3 |
| Blood antibody titer to soy protein | 4.2 | 6.7 |
| Villi height, um | 230 | 175 |
Kansas State University. |
||
【大豆卵磷脂成份和功能】
卵磷脂(Lecithin),亦是取自黃豆中的一項精華產品,自18%之黃豆油中提煉之0.5%之卵磷脂,其產品可分為粉狀及液狀,且成份如(粉狀):
(1)PHOSPHOLIPIDS 70 mgs/100gm
(2)TRIGLYCERIDES 3gm/100gm
(3)LINOLEIC ACID 58.9 gm/100gm
(4)LINOLENIC ACID 7.0 gm/100gm
(5)INOSITOL 2.2 gm/100gm
(6)熱能 6000-6500 Kcal/kg
功用
(1)提供前後期乳豬所需之脂肪酸。
(2)乳化飼料中之油類成份,脂肪在小豬腸胃中易於吸收。
(3)擴散作用使脂肪更均勻的混合於飼料中。
據美國ADM動物保健營養之研究報告所得:以卵磷脂加入黃豆油、椰子油及豬油於前後期乳豬飼料中,與對照組比較進行實驗結果顯示:其每天增重超越對照組高達30%。
由此,可證明若是添加高量之油脂,必須加入乳化作用之lecithin方為上策。
所以,粉狀卵磷脂添加於小豬料,因為可乳化飼料中脂肪,提高脂肪消化率,另外,磷的消化率也可提高,改善每日增重及飼料效率。
結論
1. 如何降低養豬成本是未來大家努力的方向。
2. 所以,小豬飼養S.E.W.系統將是未來的趨勢。
3. 高品質教槽料原料的選擇非常重要,特別是抵抗營養成份原料及提高油脂乳化效果的使用,將是達到S.E.S.必需考慮的。
(全能飼料營養技術研討會)
【大豆卵磷脂對小豬的使用及其效果】
| Body weight development of piglets receiving de-oiled lecithin supplement. | ||||
| Group No. of piglets |
Control 50
|
2g/kg ration 50 |
4g/kg ration 50 |
6g/kg ration 50 |
| Average daily gain, g | 470.2±31 | 515.0±31 | 534±31 | 550.9±31 |
| Relative gain, g | 100.0 | 109.53 | 113.70 | 117.16 |
| Feed consumption and feed conversion rate of piglet receiving de-oiled lecithin supplement. | ||||
| Group No. of piglets |
Control 50
|
2g/kg ration 50 |
4g/kg ration 50 |
6g/kg ration 50 |
| Feed conversion, kg/kg | 1.74b±0.15 | 1.61b±0.12 | 1.55±0.10bc | 1.53c±31 |
| Relative feed conversion, kg | 100.0 | 92.5 | 89.1 | 87.9 |
飼料營養雜誌(p.4∼24)─傅世雄.九五年第九期
Copyright © 1998 ![]() 茂群峪畜牧網.
本網站圖文係屬茂群峪有限公司,內文之版權為該雜誌社所
茂群峪畜牧網.
本網站圖文係屬茂群峪有限公司,內文之版權為該雜誌社所
有,非經本公司及該雜誌社正式書面同意,不得將全部或部分內容,
轉載於任何形式媒體
※ 最佳解析度 800x600
Copyright © 1998
MiobufferCo., Ltd. All rights reserved.
Unauthorized copying and reproduction is prohibited. All trademarks property of their
respective holders.